Nigeria MDGs Information System (NMIS)

Student Eucharia Ekwealor in the newly renovated
Christ the King College classroom block, Umuem, Anambra West LGA
Photo Courtesy of OSSSAP-MDGs
The Nigerian Government has committed $1.2 billion USD to achieving the Millennium Development Goals. In an effort to regulate and most effectively use this funding, the Office of the Senior Special Assistant to the President on the Millennium Development Goals (OSSAP-MDGs) created the Conditional Grants Scheme (CGS). Through this scheme, funds are released to Local Government Areas (LGAs) to be used for specific, approved purposes geared towards reducing poverty and improving education and public health, and that they be matched by local funds.
In order to support the CGS, and as part of their goal to promote the use of data in the local planning process, OSSAP-MDGs in partner with SEL undertook a rigorous, geo-referenced baseline facility inventory across Nigeria spanning from 2009 to 2011 with a supporting collection in 2014. The aim of this survey effort was to collect geo-referenced facility-level data for all of the nation’s health, education and water facilities. This data can inform level, state, and federal interventions towards closing gaps and improving indicators targeted at achieving the MDGs.
Project type: ICT4D
Location: Nigeria
Partners:
OSSAP-MDGS
Menu:
Data Gathering and Analysis
NMIS Data
Papers
Related Blog Entries
The end result is an online portal, the Nigeria MDG Information System (NMIS), that displays all of the data collected. NMIS has proven to be an invaluable planning tool for local government areas. In Summer 2014, OSSAP will take this initiative further and open the data to the public. The hope is to encourage and help other organizations better plan future infrastructure and move Nigeria closer to achieving the MDGs. It is designed to be used by planners, researchers and the broader global development community.
Data Gathering and Analysis

Technical Assistants using their Android phones during the practical on-the-ground data collection exercise at Dobi Primary School, Gwagwalada LGA, and Federal Capital Territory, Nigeria. (Photo Courtesy of Angelique Mahal)
Gathering data for NMIS was an iterative process, involving 3 separate surveys and collections. Trained enumerators collected data on Android-based smartphones using formhub, a tool specifically developed by SEL to provide fast, flexible and reliable mobile data collection, even while offline.
Before each survey round, experts thoroughly discussed content, wording, and intention for every question selected and support was provided for enumerators. After each round, a period of data cleaning was followed by substantial analysis, which revealed important information about the facilities being surveyed and helped refine survey methodologies for future data collection efforts.
The Core Indicator Survey, completed in Spring of 2014 was employed to “mop-up” the facilities not surveyed during the baseline data gathering effort in 2012 (both missed facilities as well as those built since then). This is the most streamlined survey to-date. In it, we have reduced the total number of questions significantly, refined questions with difficult or unfamiliar wording and removed redundancies. We focused on data points and indicators that have the most impact on planning.
OSSAP-MDGs data collection efforts were augmented by the following external data sources in order to form the indicators on NMIS:
- HNLSS (2008-2009)
- DHS (2008)
- School Census (2005)
- HSS (2005)
- Population Census (2003)
NMIS Data
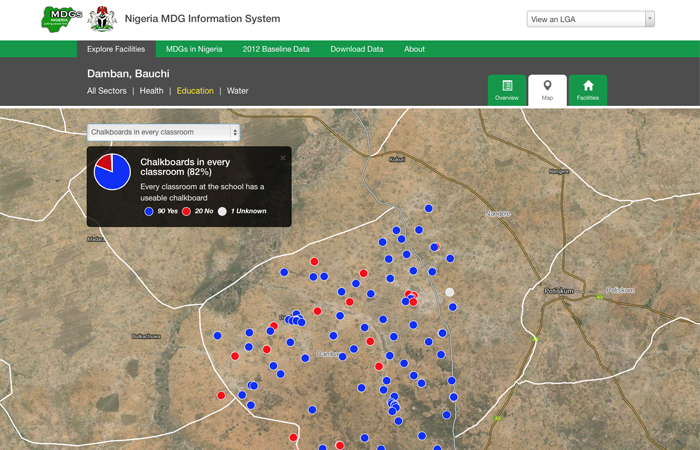
Education map view displaying number of schools with chalkboards in every classroom in Damban, Bauchi
The data collected and found on NMIS includes geo-location, type of facility, equipment, services offered, staffing, functionality and many other important parameters. Users can view critical indicators of progress for health, education and water of an entire Local Government Area, filter content by sector, view a map of facility locations or get an in-depth look at each facility. NMIS highlights specific indicators used to inform decisions on how to bridge gaps to achieve goals on a number of levels, local to federal.
Papers
Information systems for monitoring, evaluation, execution and tracking
Highlights cell phones’ use in data and information systems for smarter development


